Defining a SQL Script for an Action
Follow this procedure to define a SQL statement for index, table,
and task actions.
After completing this procedure, proceed to "Assigning an Action to a Repository
Object".
For more information about Index, Table and Task actions, see "Overview of Index,
Table and Task Actions".
To define a SQL statement for an action
1. From the Tools menu, select Seed Data, then select
one of the following:
■ Index Actions
■ Table Actions
■ Task Actions
The Actions dialog box opens.
2. In the toolbar, click New.
3. In the new record field, enter a name for the
action, and then click Save.
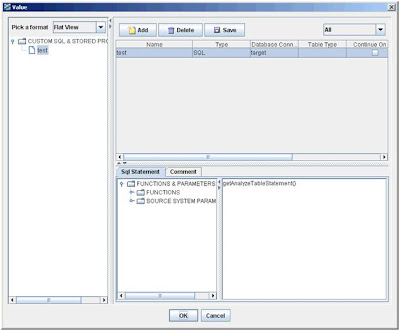
4. Double-click in the Value field.
The Value dialog box appears.
Defining a SQL Script for an Action
About
Index, Table and Task Actions 7-3
5. Select a format for the tree view.
■ Flat view displays the SQL entries in a list format in their order
of execution.
■ Category view displays the entries by the categories SQL and
Stored
Procedure.
You can reorder the entries in the tree by dragging and dropping
them.
6. Click Add.
7. In the new record field, enter or select the
appropriate information.
Field
Description
Name Logical
name of the SQL block.
Type SQL
or Stored procedure
Database
Connection
Type
Should be
used only for SQL types (not stored procedures). Defines which database the SQL
statement will run against.
Possible
values are:
Source -
SQL runs against the source connection
defined
for the task.
Target -
SQL runs against the source connection
defined
for the task.
Both -
SQL runs against both the source and
target
connection.
Table
Connection - SQL runs against the
table-specific
connection if a separate table
connection
is available.
Table
Type Specifies the table type against which the SQL
will run.
Possible
values are:
All
Source - SQL runs against all source tables
defined
for the task.
All
Target - SQL runs against all target tables
defined
for the task.
Source
Lookup - SQL runs against all the source
lookup
tables defined for the task.
Source
Primary - SQL runs against all the source
primary
tables defined for the task.
Source
Auxiliary - SQL runs against all the source
auxiliary
tables defined for the task.
Continue
on Fail Specifies
whether an execution should proceed if
a given
SQL block fails.
Retries Specifies how many retries
are allowed. If the
number is
not positive, a default number of one
(1) will
be used.
Valid
Database Platforms Specifies the
valid database platforms against
which the
SQL will run. If this field is left empty,
the SQL
can be run against any database.
8. In the lower-right side text box, enter a SQL
statement.
The SQL Statement tab to the left of the text box lists all the
supported SQL
functions and DAC source system parameters that you can use in
constructing
custom SQLs. Double-click a function or source system parameter to
move it into
the text box.
For a description of the available functions, see "Functions for Use with Actions".
The source systems parameters list contains the names of all
source system
parameters defined in the DAC Repository, with the prefix @DAC_.
During
runtime, the DAC Server resolves the source system parameter and
replaces its
name with the runtime value.
For an example of how to use a source system parameter in a SQL
statement, see
"Example of How to Use a DAC Source System Parameter in
an Action".
9. (Optional) Enter a comment about the SQL in the
Comment tab.
10. Click OK.
Note: You can add multiple SQL statements and stored
procedures
to a single action.
11. To assign this action to a repository object,
proceed to "Assigning an Action to a
Repository Object".
No comments:
Post a Comment